Homework Answers
Question N0 15
Given
Mean (Xabr)=2.64 Miles
Standard Deviation ( )=0.15
miles
)=0.15
miles
Sample size = 43
For 95% confidence level Z=1.96 (Refer standard normal table)
We have
Z = (X - Xbar)/
1.96 = (X- 2.64)/0.15
X = 1.96*0.15 + 2.64 =2.93
Therefore for 95% confidence level mean =2.93
Correct Answer is
Z table
Note :
(a) T -table shows probablity under probablity density funtion.
(b) F-table shows a probability density function that is used especially in analysis of variance.
Add Answer to:
The number of miles traveled by birds is known to be normally distributed. A random sample...
IQ scores are normally distributed with a mean of 100 and a standard deviation of 15....
IQ scores are normally distributed with a mean of 100 and a standard deviation of 15. A sample of 10 children in a gifted learner program are found to have a mean IQ of 106. Use a z-test to determine if this is significantly different from the normal population mean. What are your specific null and alternative hypothesis? Z=+ - 1.96 standard deviation m= 4.743 Z= 1.26 Will you reject or retain the null hypothesis? We will retain the null...
Consider the following competing hypotheses and accompanying sample data drawn independently from normally distributed populations. (You...
 Consider the following competing hypotheses and accompanying sample data drawn independently from normally distributed populations. (You may find it useful to reference the appropriate table: z table or t table) Ho: H1-Hu2 0 HA: H1 Hz< e 251 252 s1 39 s=19 n1=7 n 7 a-1. Calculate the value of the test statistic under the assumption that the population variances are equal. (Negative values should be indicated by a minus sign. Round all intermediate calculations to at least 4 decimal...
Consider the following competing hypotheses and accompanying sample data drawn independently from normally distributed populations. (You may find it useful to reference the appropriate table: z table or t table) Ho: H1-Hu2 0 HA: H1 Hz< e 251 252 s1 39 s=19 n1=7 n 7 a-1. Calculate the value of the test statistic under the assumption that the population variances are equal. (Negative values should be indicated by a minus sign. Round all intermediate calculations to at least 4 decimal...
Given a normally distributed population with known standard deviation of o = 4, and suppose we...
 Given a normally distributed population with known standard deviation of o = 4, and suppose we would like to test Hair = 14 against H.:p> 14 and significance level a = .05 a) If the null hypothesis is true, what is the probability that we would reject it in favor of the alternative hypothesis? b) Taking a random sample of n= 10 from the population and find that the sample mean is a 16.5. Give the observed value z of...
Given a normally distributed population with known standard deviation of o = 4, and suppose we would like to test Hair = 14 against H.:p> 14 and significance level a = .05 a) If the null hypothesis is true, what is the probability that we would reject it in favor of the alternative hypothesis? b) Taking a random sample of n= 10 from the population and find that the sample mean is a 16.5. Give the observed value z of...
Consider the following data drawn independently from normally distributed populations: (You may find it useful to...
 Consider the following data drawn independently from normally distributed populations: (You may find it useful to reference the appropriate table: z table or t table) X1 = 27.1 012 = 89.5 n1 = 25 X2 = 30.3 022 = 92.3 n2 = 31 a. Construct the 90% confidence interval for the difference between the population means. (Negative values should be indicated by a minus sign. Round all intermediate calculations to at least 4 decimal places and final answers to 2...
Consider the following data drawn independently from normally distributed populations: (You may find it useful to reference the appropriate table: z table or t table) X1 = 27.1 012 = 89.5 n1 = 25 X2 = 30.3 022 = 92.3 n2 = 31 a. Construct the 90% confidence interval for the difference between the population means. (Negative values should be indicated by a minus sign. Round all intermediate calculations to at least 4 decimal places and final answers to 2...
Consider the following data drawn independently from normally distributed populations: (You may find it useful to...
 Consider the following data drawn independently from normally distributed populations: (You may find it useful to reference the appropriate table: z table or t table) 21 = 29.8 012 - 95.3 nu = 34 22 = 32.4 oz? = 91.6 ng = 29 a. Construct the 99% confidence interval for the difference between the population means. (Negative values should be indicated by a minus sign. Round all intermediate calculations to at least 4 decimal places and final answers to 2...
Consider the following data drawn independently from normally distributed populations: (You may find it useful to reference the appropriate table: z table or t table) 21 = 29.8 012 - 95.3 nu = 34 22 = 32.4 oz? = 91.6 ng = 29 a. Construct the 99% confidence interval for the difference between the population means. (Negative values should be indicated by a minus sign. Round all intermediate calculations to at least 4 decimal places and final answers to 2...
The following information was obtained from independent random samples. Assume normally populations with equal Sample 1...
 The following information was obtained from independent random samples. Assume normally populations with equal Sample 1 Sample 2 12 Sample Size 10 Sample Mean 52 Sample Variance 85 We are interested in testing Hai sample 1 -Hsample 2 0 Step 2 of 3: Determine the p-value for the test. TablesKeypad Answer 1 Point Next Prev O p-value c 0.025 0.025< p-value <0.05 Op-value <0.1 。p-value > 0.2 None of the above o 2019 8 3 of 3 The following information...
The following information was obtained from independent random samples. Assume normally populations with equal Sample 1 Sample 2 12 Sample Size 10 Sample Mean 52 Sample Variance 85 We are interested in testing Hai sample 1 -Hsample 2 0 Step 2 of 3: Determine the p-value for the test. TablesKeypad Answer 1 Point Next Prev O p-value c 0.025 0.025< p-value <0.05 Op-value <0.1 。p-value > 0.2 None of the above o 2019 8 3 of 3 The following information...
Consider the following data drawn independently from normally distributed populations: (You may find it useful to...
Consider the following data drawn independently from normally distributed populations: (You may find it useful to reference the appropriate table: z table or t table) x−1x−1 = 27.7 x−2x−2 = 30.1 σ12 = 92.8 σ22 = 87.5 n1 = 24 n2 = 33 a. Construct the 99% confidence interval for the difference between the population means. (Negative values should be indicated by a minus sign. Round all intermediate calculations to at least 4 decimal places and final answers to 2...
Consider the following competing hypotheses and accompanying sample data drawn independently from normally distributed populations. (You may find it useful to reference the appropriate table: z table or t table)
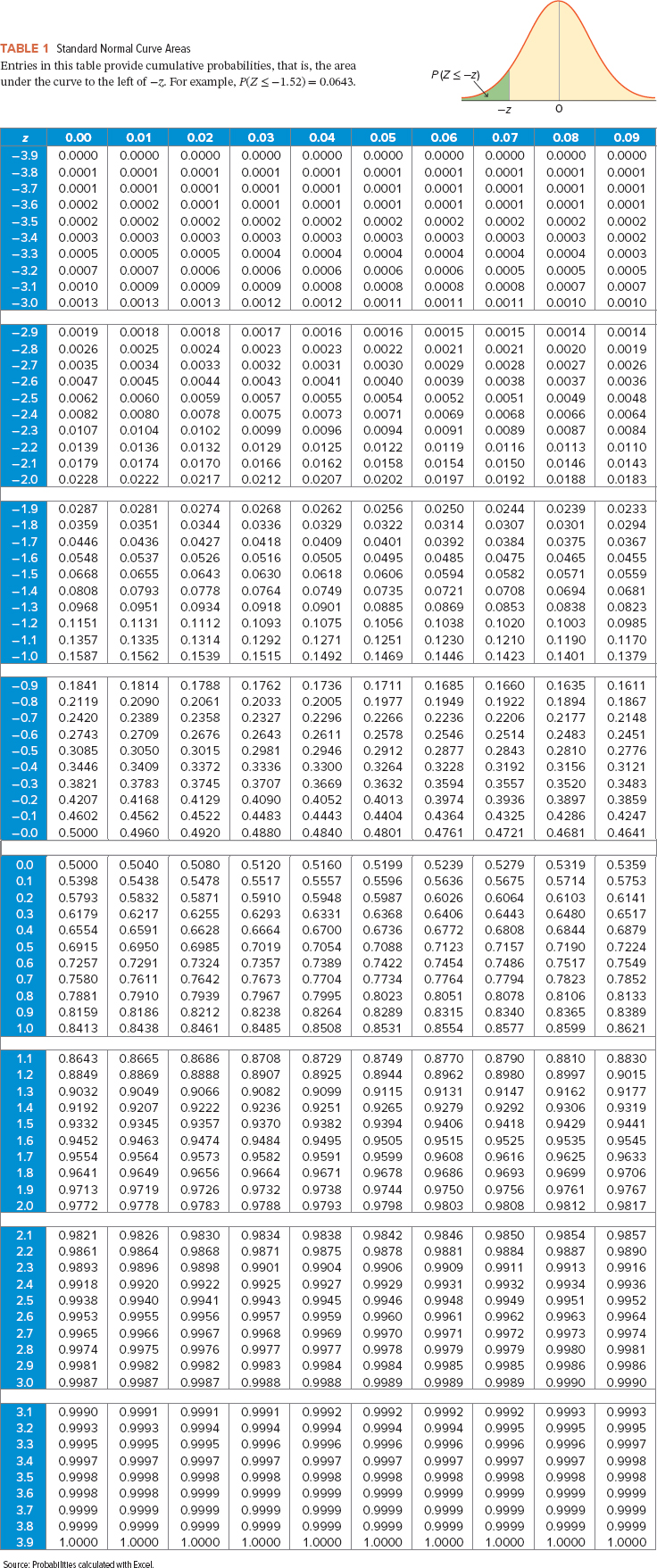 Consider the following competing hypotheses and accompanying sample data drawn independently from normally distributed populations. (You may find it useful to reference the appropriate table: z table or t table) H0: μ1 − μ2 ≥ 0HA: μ1 − μ2 < 0 x¯1x¯1= 249x−2x−2= 262s1 = 35s2 = 23n1 = 10n2 = 10a-1. Calculate the value of the test statistic under the assumption that the population variances are equal. (Negative values should be indicated by a minus sign. Round all intermediate calculations to at least 4 decimal places and final answer to 3 decimal places.) a-2. Find the p-value. multiple choice 1p-value < 0.010.01 ≤ p-value...
Consider the following competing hypotheses and accompanying sample data drawn independently from normally distributed populations. (You may find it useful to reference the appropriate table: z table or t table) H0: μ1 − μ2 ≥ 0HA: μ1 − μ2 < 0 x¯1x¯1= 249x−2x−2= 262s1 = 35s2 = 23n1 = 10n2 = 10a-1. Calculate the value of the test statistic under the assumption that the population variances are equal. (Negative values should be indicated by a minus sign. Round all intermediate calculations to at least 4 decimal places and final answer to 3 decimal places.) a-2. Find the p-value. multiple choice 1p-value < 0.010.01 ≤ p-value...
A random sample of size n= 15 obtained from a population that is normally distributed results...
 A random sample of size n= 15 obtained from a population that is normally distributed results in a sample mean of 45.8 and sample standard deviation 12.2. An independent sample of size n = 20 obtained from a population that is normally distributed results in a sample mean of 51.9 and sample standard deviation 14.6. Does this constitute sufficient evidence to conclude that the population means differ at the a = 0.05 level of significance? Click here to view the...
A random sample of size n= 15 obtained from a population that is normally distributed results in a sample mean of 45.8 and sample standard deviation 12.2. An independent sample of size n = 20 obtained from a population that is normally distributed results in a sample mean of 51.9 and sample standard deviation 14.6. Does this constitute sufficient evidence to conclude that the population means differ at the a = 0.05 level of significance? Click here to view the...
For a random sample of 36 data pairs, the sample mean of the differences was 0.72....
 For a random sample of 36 data pairs, the sample mean of the differences was 0.72. The sample standard deviation of the differences was 2. At the 5% level of significance, test the claim that the population mean of the differences is different from 0. (a) Is it appropriate to use a Student's t distribution for the sample test statistic? Explain. No, the sample size is not larger than 30. Yes, the sample size is larger than 30. No, the...
For a random sample of 36 data pairs, the sample mean of the differences was 0.72. The sample standard deviation of the differences was 2. At the 5% level of significance, test the claim that the population mean of the differences is different from 0. (a) Is it appropriate to use a Student's t distribution for the sample test statistic? Explain. No, the sample size is not larger than 30. Yes, the sample size is larger than 30. No, the...
Most questions answered within 3 hours.
-
A box contains 14 large marbles and 19 small marbles. Each
marble is either green or...
asked 5 minutes ago -
The results of a one-sample t test were t (18) = 2.11,
p < 0.05. In...
asked 15 minutes ago -
What kind of share-based compensation does the company have for
Verizon? What was compensation expense for...
asked 23 minutes ago -
Place each of the following transactions in one of the four
components of expenditure: (remember it...
asked 31 minutes ago -
Find the optimal binary symbol code using the Huffman coding
algorithm. Draw the Huffman tree (show...
asked 34 minutes ago -
Using Rhodes Corporation’s financial statements (shown after
part f), answer the following questions.
a. What is...
asked 33 minutes ago -
Viewers of the ABC news segment may use ___________ to make
generalization about what the individual...
asked 43 minutes ago -
Which of the following captures Locke’s response to Hobbes on
the issue of the enforcement of...
asked 50 minutes ago -
another 515 students are selected at random from florida. they are
given a 3-hour preparation course...
asked 1 hour ago -
A regional distributor deals with a product ABC that has an
annual demand of 3000 unit....
asked 2 hours ago -
You have a 825.3 mL sample of 2.754 M HA (Ka =
4.49⋅10−4). Calculate the pH...
asked 5 hours ago -
The blues made its way into many kinds of music. Eric Clapton,
The Beatles, and Elvis...
asked 7 hours ago

 Consider the following competing hypotheses and accompanying sample data drawn independently from normally distributed populations. (You may find it useful to reference the appropriate table: z table or t table) Ho: H1-Hu2 0 HA: H1 Hz< e 251 252 s1 39 s=19 n1=7 n 7 a-1. Calculate the value of the test statistic under the assumption that the population variances are equal. (Negative values should be indicated by a minus sign. Round all intermediate calculations to at least 4 decimal...
Consider the following competing hypotheses and accompanying sample data drawn independently from normally distributed populations. (You may find it useful to reference the appropriate table: z table or t table) Ho: H1-Hu2 0 HA: H1 Hz< e 251 252 s1 39 s=19 n1=7 n 7 a-1. Calculate the value of the test statistic under the assumption that the population variances are equal. (Negative values should be indicated by a minus sign. Round all intermediate calculations to at least 4 decimal...
 Given a normally distributed population with known standard deviation of o = 4, and suppose we would like to test Hair = 14 against H.:p> 14 and significance level a = .05 a) If the null hypothesis is true, what is the probability that we would reject it in favor of the alternative hypothesis? b) Taking a random sample of n= 10 from the population and find that the sample mean is a 16.5. Give the observed value z of...
Given a normally distributed population with known standard deviation of o = 4, and suppose we would like to test Hair = 14 against H.:p> 14 and significance level a = .05 a) If the null hypothesis is true, what is the probability that we would reject it in favor of the alternative hypothesis? b) Taking a random sample of n= 10 from the population and find that the sample mean is a 16.5. Give the observed value z of...
 Consider the following data drawn independently from normally distributed populations: (You may find it useful to reference the appropriate table: z table or t table) X1 = 27.1 012 = 89.5 n1 = 25 X2 = 30.3 022 = 92.3 n2 = 31 a. Construct the 90% confidence interval for the difference between the population means. (Negative values should be indicated by a minus sign. Round all intermediate calculations to at least 4 decimal places and final answers to 2...
Consider the following data drawn independently from normally distributed populations: (You may find it useful to reference the appropriate table: z table or t table) X1 = 27.1 012 = 89.5 n1 = 25 X2 = 30.3 022 = 92.3 n2 = 31 a. Construct the 90% confidence interval for the difference between the population means. (Negative values should be indicated by a minus sign. Round all intermediate calculations to at least 4 decimal places and final answers to 2...
 Consider the following data drawn independently from normally distributed populations: (You may find it useful to reference the appropriate table: z table or t table) 21 = 29.8 012 - 95.3 nu = 34 22 = 32.4 oz? = 91.6 ng = 29 a. Construct the 99% confidence interval for the difference between the population means. (Negative values should be indicated by a minus sign. Round all intermediate calculations to at least 4 decimal places and final answers to 2...
Consider the following data drawn independently from normally distributed populations: (You may find it useful to reference the appropriate table: z table or t table) 21 = 29.8 012 - 95.3 nu = 34 22 = 32.4 oz? = 91.6 ng = 29 a. Construct the 99% confidence interval for the difference between the population means. (Negative values should be indicated by a minus sign. Round all intermediate calculations to at least 4 decimal places and final answers to 2...
 The following information was obtained from independent random samples. Assume normally populations with equal Sample 1 Sample 2 12 Sample Size 10 Sample Mean 52 Sample Variance 85 We are interested in testing Hai sample 1 -Hsample 2 0 Step 2 of 3: Determine the p-value for the test. TablesKeypad Answer 1 Point Next Prev O p-value c 0.025 0.025< p-value <0.05 Op-value <0.1 。p-value > 0.2 None of the above o 2019 8 3 of 3 The following information...
The following information was obtained from independent random samples. Assume normally populations with equal Sample 1 Sample 2 12 Sample Size 10 Sample Mean 52 Sample Variance 85 We are interested in testing Hai sample 1 -Hsample 2 0 Step 2 of 3: Determine the p-value for the test. TablesKeypad Answer 1 Point Next Prev O p-value c 0.025 0.025< p-value <0.05 Op-value <0.1 。p-value > 0.2 None of the above o 2019 8 3 of 3 The following information...
 A random sample of size n= 15 obtained from a population that is normally distributed results in a sample mean of 45.8 and sample standard deviation 12.2. An independent sample of size n = 20 obtained from a population that is normally distributed results in a sample mean of 51.9 and sample standard deviation 14.6. Does this constitute sufficient evidence to conclude that the population means differ at the a = 0.05 level of significance? Click here to view the...
A random sample of size n= 15 obtained from a population that is normally distributed results in a sample mean of 45.8 and sample standard deviation 12.2. An independent sample of size n = 20 obtained from a population that is normally distributed results in a sample mean of 51.9 and sample standard deviation 14.6. Does this constitute sufficient evidence to conclude that the population means differ at the a = 0.05 level of significance? Click here to view the...
 For a random sample of 36 data pairs, the sample mean of the differences was 0.72. The sample standard deviation of the differences was 2. At the 5% level of significance, test the claim that the population mean of the differences is different from 0. (a) Is it appropriate to use a Student's t distribution for the sample test statistic? Explain. No, the sample size is not larger than 30. Yes, the sample size is larger than 30. No, the...
For a random sample of 36 data pairs, the sample mean of the differences was 0.72. The sample standard deviation of the differences was 2. At the 5% level of significance, test the claim that the population mean of the differences is different from 0. (a) Is it appropriate to use a Student's t distribution for the sample test statistic? Explain. No, the sample size is not larger than 30. Yes, the sample size is larger than 30. No, the...