

added part a of the question for clarity
Homework Answers
Q1, a) Please find the answer as below image,
 Q2, C, Base on the analysis of given helix
structure
Q2, C, Base on the analysis of given helix
structure
i) The nuber of amino acid resudue per turn in the alpha helix is 3.6
ii) The per residue rise is 1.5 Å which results the rise per turn is 5.4 Å.
iii) The psi and phi values for the alpha helix is t30 degree and 140 degree respectively.
d) i)
The below image explain the antiparallel beta strand with the hydrogen bonding is highlighed in red colur.
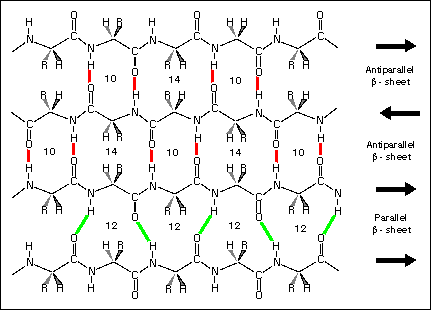
ii) There are two residues per repeat unit which gives the beta-strand a 7 Angstrom..
The anti parallel beta strand length is 7 Angstrom..
iii) The psi and phi values for the antiparallel beta pleated sheet are
psi = = -139 degree
phi = +135 degree
Add Answer to:
added part a of the question for clarity 1. Polypeptides are the natural polymer of the...
6. (a) Show the arrangement of the groups on the a carbon of the naturally occurring amino acids (draw out the stereoce...
 6. (a) Show the arrangement of the groups on the a carbon of the naturally occurring amino acids (draw out the stereocentre). (b) What is the significance of chirality in the biological world? 7. (a) Sh (a) Show the repeating unit of the polypeptide chain in a protein and indicate the peptide bond. (b) What are the following structures of a protein (i) primary, (ii) secondary, (iii) tertiary and (iv) quaternary. 1. Polypeptides are the natural polymer of the naturally...
6. (a) Show the arrangement of the groups on the a carbon of the naturally occurring amino acids (draw out the stereocentre). (b) What is the significance of chirality in the biological world? 7. (a) Sh (a) Show the repeating unit of the polypeptide chain in a protein and indicate the peptide bond. (b) What are the following structures of a protein (i) primary, (ii) secondary, (iii) tertiary and (iv) quaternary. 1. Polypeptides are the natural polymer of the naturally...
The _______ of amino acids in a protein is referred to as its primary structure
24. The _______ of amino acids in a protein is referred to as its primary structure. A) twisting B) sequencing C) folding D) none of these 25. The structure of a protein is most important because the _______ of the amino acids determines its overall shape, function and properties. A) primary, twisting B) primary, sequencing C) secondary, twisting D) secondary, folding E) none of these 26. The secondary structure of a protein is due to_______ between amino acid residues. A) hydrophobic interactions B) hydrogen bonding...
Understand alpha helices and beta pleated sheets Question How is it possible for the a-helix to have amino acids with b...
 Understand alpha helices and beta pleated sheets Question How is it possible for the a-helix to have amino acids with bulky side chains while the B-pleated sheets cannot? Select the correct answer below: O The R groups in the a-helix stabilize the structure, while they interfere with the hydrogen bonds in a B-pleated sheet. The R groups are contained inside the a-helix structure, while they interfere with the hydrogen bonds in a B- pleated sheet. O The R groups lie...
Understand alpha helices and beta pleated sheets Question How is it possible for the a-helix to have amino acids with bulky side chains while the B-pleated sheets cannot? Select the correct answer below: O The R groups in the a-helix stabilize the structure, while they interfere with the hydrogen bonds in a B-pleated sheet. The R groups are contained inside the a-helix structure, while they interfere with the hydrogen bonds in a B- pleated sheet. O The R groups lie...
which of the following is not a way in which amino acid structure in sequence might...
which of the following is not a way in which amino acid structure in sequence might affect the properties of a protein a) Amino acid side chains form peptide bonds with each other causing the molecule to twist into a secondary structure b) Amino side chains interact with each other causing polypeptides to bend into a tertiary structure c) Hydrogen bonding between every fourth amino acid results in the formation of a coil called an a helix d) Hydrogen bonding...
What happens when a primary structure forms a secondary structure? Match the words in the left...
 What happens when a primary structure forms a secondary structure? Match the words in the left column to the appropriate blanks in the sentences on the right. Make certain each sentence is complete before submitting your answer. Terms may be used once, more than once, or not at all. Reset Help carboxylic acid a helix When atoms in the backbone of a protein or peptide form within a single or between chains, a secondary structure results. The two most common...
What happens when a primary structure forms a secondary structure? Match the words in the left column to the appropriate blanks in the sentences on the right. Make certain each sentence is complete before submitting your answer. Terms may be used once, more than once, or not at all. Reset Help carboxylic acid a helix When atoms in the backbone of a protein or peptide form within a single or between chains, a secondary structure results. The two most common...
Biochemistry! Please read the whole question before answering. And please explain. 1. Read both parts A...
 Biochemistry! Please read the whole question before answering.
And please explain.
1. Read both parts A and B of question 1 before you answer either one. Draw a peptide backbone that extends for three amino acids. Label the psi, phi and omega angles, showing the direction of rotation. Indicate resonance. Draw the structure with the more likely cis or trans conformation. Indicate side chains with the letters R1, R2 and R3. A. B. Draw a second peptide below the one...
Biochemistry! Please read the whole question before answering.
And please explain.
1. Read both parts A and B of question 1 before you answer either one. Draw a peptide backbone that extends for three amino acids. Label the psi, phi and omega angles, showing the direction of rotation. Indicate resonance. Draw the structure with the more likely cis or trans conformation. Indicate side chains with the letters R1, R2 and R3. A. B. Draw a second peptide below the one...
amino acid sequence: HVSYTLTPGALDINWR For the antiparallel b-sheet sequence, sketch the structure; denote R groups as...
amino acid sequence: HVSYTLTPGALDINWR For the antiparallel b-sheet sequence, sketch the structure; denote R groups as one letter codes, hydrogen-bonds with dashed lines, and label the b-turn. Do you expect this small b-sheet to be hydrophilic, hydrophobic, or amphipathic?
Understand alpha helices and beta pleated sheets Question The coiling of an a-helix is maintained in...
 Understand alpha helices and beta pleated sheets Question The coiling of an a-helix is maintained in position by which of the following bonds? Select the correct answer below: hydrogen bonds between the oxygen atom in the carbonyl group in one amino acid and the hydrogen atom of the hydroxyl group in an R-group of another amino acid that is four amino acids farther along the chain O hydrogen bonds between the oxygen atom in the carbonyl group in one amino...
Understand alpha helices and beta pleated sheets Question The coiling of an a-helix is maintained in position by which of the following bonds? Select the correct answer below: hydrogen bonds between the oxygen atom in the carbonyl group in one amino acid and the hydrogen atom of the hydroxyl group in an R-group of another amino acid that is four amino acids farther along the chain O hydrogen bonds between the oxygen atom in the carbonyl group in one amino...
D) glycosyltransferases E) carboxypeptidase 26. What type of protein secondary structure is characterized as being highly...
 D) glycosyltransferases E) carboxypeptidase 26. What type of protein secondary structure is characterized as being highly extensible because of its coiled structure? A B-pleated sheet By double helix a-helix supercoiling local folding 27. The figure above is an example of a: A) Glycerol Sterol - Phospholipid D) Glycolipid E) Sugar 28. Long tails (relative to short fatty acid tails) of lipids that make up plasma membranes increase the viscosity of a plasma membrane due the which of the following? A)...
D) glycosyltransferases E) carboxypeptidase 26. What type of protein secondary structure is characterized as being highly extensible because of its coiled structure? A B-pleated sheet By double helix a-helix supercoiling local folding 27. The figure above is an example of a: A) Glycerol Sterol - Phospholipid D) Glycolipid E) Sugar 28. Long tails (relative to short fatty acid tails) of lipids that make up plasma membranes increase the viscosity of a plasma membrane due the which of the following? A)...
Wetan Which of the following compounds are dashed following compounds are dassted as carbonyl compounds acetic...
 Wetan Which of the following compounds are dashed following compounds are dassted as carbonyl compounds acetic acid methvi tommate 2-propanol butanal (a) only! (b) L and I) IL 111 Vand d) 1. ll. lll, and V (e) all of them 2 Kevlar is a polymer the functional groups present in Kevlar shown below! Kevlar is due to the hydrogen bonds between the polymer y er that is used in bulletproot vests and tires. Part of the strength of bonds between...
Wetan Which of the following compounds are dashed following compounds are dassted as carbonyl compounds acetic acid methvi tommate 2-propanol butanal (a) only! (b) L and I) IL 111 Vand d) 1. ll. lll, and V (e) all of them 2 Kevlar is a polymer the functional groups present in Kevlar shown below! Kevlar is due to the hydrogen bonds between the polymer y er that is used in bulletproot vests and tires. Part of the strength of bonds between...
Most questions answered within 3 hours.
-
1. What is the present value of $400, three years in the future
if the interest...
asked 2 minutes ago -
The labor force minus the number of employed equals the number
of unemployed.
a. True
b....
asked 2 hours ago -
Determine the mass in units of grams [g] of 0.49 moles [mol]
of a new fictitious...
asked 2 hours ago -
A horizontal mass of M=5kg is on a spring and stretched to
x=0.5m when released from...
asked 3 hours ago -
26 of 50
"I have worked at the Arizona Humane Society for ten years, and
have...
asked 4 hours ago -
Compare and contrast zero based budgeting and incremental (or
base year) budgeting.
asked 4 hours ago -
4 pts 10. Which of the following hypothesis would be MOST
difficult to test experimentally? Group...
asked 4 hours ago -
A business owner makes 1,000 items a day. Each day he or she
contributes eight hours...
asked 4 hours ago -
A
circular loop in the plane of a paper lies inca0.65 T magnetic
field pointing into...
asked 4 hours ago -
A business owner is trying to decide whether to buy, rent, or
lease office space and...
asked 4 hours ago -
Thermal Storage Solar heating of a house is much more efficient
if there is a way...
asked 4 hours ago -
Considering the “fits” for group and job design dimensions,
suppose you had 12 employees with different...
asked 4 hours ago
 6. (a) Show the arrangement of the groups on the a carbon of the naturally occurring amino acids (draw out the stereocentre). (b) What is the significance of chirality in the biological world? 7. (a) Sh (a) Show the repeating unit of the polypeptide chain in a protein and indicate the peptide bond. (b) What are the following structures of a protein (i) primary, (ii) secondary, (iii) tertiary and (iv) quaternary. 1. Polypeptides are the natural polymer of the naturally...
6. (a) Show the arrangement of the groups on the a carbon of the naturally occurring amino acids (draw out the stereocentre). (b) What is the significance of chirality in the biological world? 7. (a) Sh (a) Show the repeating unit of the polypeptide chain in a protein and indicate the peptide bond. (b) What are the following structures of a protein (i) primary, (ii) secondary, (iii) tertiary and (iv) quaternary. 1. Polypeptides are the natural polymer of the naturally...
 Understand alpha helices and beta pleated sheets Question How is it possible for the a-helix to have amino acids with bulky side chains while the B-pleated sheets cannot? Select the correct answer below: O The R groups in the a-helix stabilize the structure, while they interfere with the hydrogen bonds in a B-pleated sheet. The R groups are contained inside the a-helix structure, while they interfere with the hydrogen bonds in a B- pleated sheet. O The R groups lie...
Understand alpha helices and beta pleated sheets Question How is it possible for the a-helix to have amino acids with bulky side chains while the B-pleated sheets cannot? Select the correct answer below: O The R groups in the a-helix stabilize the structure, while they interfere with the hydrogen bonds in a B-pleated sheet. The R groups are contained inside the a-helix structure, while they interfere with the hydrogen bonds in a B- pleated sheet. O The R groups lie...
 What happens when a primary structure forms a secondary structure? Match the words in the left column to the appropriate blanks in the sentences on the right. Make certain each sentence is complete before submitting your answer. Terms may be used once, more than once, or not at all. Reset Help carboxylic acid a helix When atoms in the backbone of a protein or peptide form within a single or between chains, a secondary structure results. The two most common...
What happens when a primary structure forms a secondary structure? Match the words in the left column to the appropriate blanks in the sentences on the right. Make certain each sentence is complete before submitting your answer. Terms may be used once, more than once, or not at all. Reset Help carboxylic acid a helix When atoms in the backbone of a protein or peptide form within a single or between chains, a secondary structure results. The two most common...
 Biochemistry! Please read the whole question before answering.
And please explain.
1. Read both parts A and B of question 1 before you answer either one. Draw a peptide backbone that extends for three amino acids. Label the psi, phi and omega angles, showing the direction of rotation. Indicate resonance. Draw the structure with the more likely cis or trans conformation. Indicate side chains with the letters R1, R2 and R3. A. B. Draw a second peptide below the one...
Biochemistry! Please read the whole question before answering.
And please explain.
1. Read both parts A and B of question 1 before you answer either one. Draw a peptide backbone that extends for three amino acids. Label the psi, phi and omega angles, showing the direction of rotation. Indicate resonance. Draw the structure with the more likely cis or trans conformation. Indicate side chains with the letters R1, R2 and R3. A. B. Draw a second peptide below the one...
 Understand alpha helices and beta pleated sheets Question The coiling of an a-helix is maintained in position by which of the following bonds? Select the correct answer below: hydrogen bonds between the oxygen atom in the carbonyl group in one amino acid and the hydrogen atom of the hydroxyl group in an R-group of another amino acid that is four amino acids farther along the chain O hydrogen bonds between the oxygen atom in the carbonyl group in one amino...
Understand alpha helices and beta pleated sheets Question The coiling of an a-helix is maintained in position by which of the following bonds? Select the correct answer below: hydrogen bonds between the oxygen atom in the carbonyl group in one amino acid and the hydrogen atom of the hydroxyl group in an R-group of another amino acid that is four amino acids farther along the chain O hydrogen bonds between the oxygen atom in the carbonyl group in one amino...
 D) glycosyltransferases E) carboxypeptidase 26. What type of protein secondary structure is characterized as being highly extensible because of its coiled structure? A B-pleated sheet By double helix a-helix supercoiling local folding 27. The figure above is an example of a: A) Glycerol Sterol - Phospholipid D) Glycolipid E) Sugar 28. Long tails (relative to short fatty acid tails) of lipids that make up plasma membranes increase the viscosity of a plasma membrane due the which of the following? A)...
D) glycosyltransferases E) carboxypeptidase 26. What type of protein secondary structure is characterized as being highly extensible because of its coiled structure? A B-pleated sheet By double helix a-helix supercoiling local folding 27. The figure above is an example of a: A) Glycerol Sterol - Phospholipid D) Glycolipid E) Sugar 28. Long tails (relative to short fatty acid tails) of lipids that make up plasma membranes increase the viscosity of a plasma membrane due the which of the following? A)...
 Wetan Which of the following compounds are dashed following compounds are dassted as carbonyl compounds acetic acid methvi tommate 2-propanol butanal (a) only! (b) L and I) IL 111 Vand d) 1. ll. lll, and V (e) all of them 2 Kevlar is a polymer the functional groups present in Kevlar shown below! Kevlar is due to the hydrogen bonds between the polymer y er that is used in bulletproot vests and tires. Part of the strength of bonds between...
Wetan Which of the following compounds are dashed following compounds are dassted as carbonyl compounds acetic acid methvi tommate 2-propanol butanal (a) only! (b) L and I) IL 111 Vand d) 1. ll. lll, and V (e) all of them 2 Kevlar is a polymer the functional groups present in Kevlar shown below! Kevlar is due to the hydrogen bonds between the polymer y er that is used in bulletproot vests and tires. Part of the strength of bonds between...