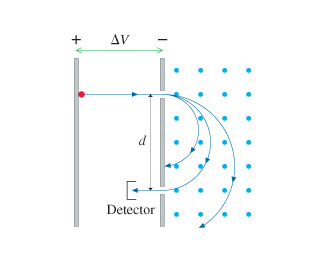
(Figure 1) shows a mass spectrometer, an analytical instrument
used to identify the various molecules in a sample by measuring
their charge-to-mass ratio q/m. The sample is ionized, the positive
ions are accelerated (starting from rest) through a potential
difference ΔV, and they then enter a region of uniform magnetic
field. The field bends the ions into circular trajectories, but
after just half a circle they either strike the wall or pass
through a small opening to a detector. As the accelerating voltage
is slowly increased, different ions reach the detector and are
measured. Consider a mass spectrometer with a 200.00 mT magnetic
field and an 8.0000 cm spacing between the entrance and exit
holes.
To five significant figures, what accelerating potential
difference ΔV is required to detect the ion O+2? The masses of the
atoms are shown in the table; the mass of the missing electron is
less than 0.001 u and is not relevant at this level of precision.
Use the following constants: 1 u = 1.6605×10−27kg, e =
1.6022×10−19C.
Atomic masses
12C 12.000 u
14N 14.003 u
16O 15.992 u
Express your answer to five significant figures and include the
appropriate units.
What accelerating potential difference ΔV is required to detect N+2?
Although N+2 and CO+ both have a nominal molecular mass of 28, they are easily distinguished by virtue of their slightly different accelerating voltages. What accelerating potential difference ΔV is required to detect CO+?
Homework Answers
a )
r = 8 / 2
= 4 cm
= 0.04 m
r = m v / q B
we have ΔV = r2 B2 q / 2 m
= 0.042 x 0.22 x q / 2 m
ΔV = 32 x 10-6 ( q/m )
ΔV O2+ = 32 x 10-6 x 1.6 x 10-19 / 2 x 15.992 x 1.67 x 10-27
ΔV O2+ = 96.537 volts
b )
ΔV N2+ = 32 x 10-6 x 1.6 x 10-19 / 2 x 14.003 x 1.67 x 10-27
ΔV O2+ = 110.249 volts
c )
ΔV CO+ = 32 x 10-6 x 1.6 x 10-19 / ( 12 + 15.992 ) x 1.67 x 10-27
ΔV CO+ = 110.3046 volts
Add Answer to:
(Figure 1) shows a mass spectrometer, an analytical instrument
used to identify the various molecules in...
The figure below shows a mass spectrometer, an analytical instrument used to identify the various molecules...
The figure below shows a mass spectrometer, an analytical instrument used to identify the various molecules in a sample by measuring their charge-to-mass ratio e/m. The sample is ionized, the positive ions are accelerated (starting from rest) through a potential difference ΔV, and they then enter a region of uniform magnetic field. The field bends the ions into circular trajectories, but after just half a circle they either strike the wall or pass through a small opening to a detector....
To five significant figures, what accelerating potential difference AV is required to detect the ion 0...
 To five significant figures, what accelerating potential difference AV is required to detect the ion 0 ? The masses of the atoms are shown in the table; the mass of the missing electron is less than 0.001 u and is not relevant at this level of precision. Use the following constants: 1 u = 1.6605 x 10-27 kg, e = 1.6022 x 10-19 C. (Figure 1) shows a mass spectrometer, an analytical instrument used to identify the various molecules in...
To five significant figures, what accelerating potential difference AV is required to detect the ion 0 ? The masses of the atoms are shown in the table; the mass of the missing electron is less than 0.001 u and is not relevant at this level of precision. Use the following constants: 1 u = 1.6605 x 10-27 kg, e = 1.6022 x 10-19 C. (Figure 1) shows a mass spectrometer, an analytical instrument used to identify the various molecules in...
• The figure shows the essentials of a mass spectrometer, which can be used to measure...
 • The figure shows the essentials of a mass spectrometer, which can be used to measure the mass of an ion; an ion of mass m (to be measured) and charge q is produced in source S. The initially stationary ion is accelerated by the electric field due to a potential difference V. The ion leaves S and enters a separator chamber in which a uniform magnetic field is perpendicular to the path of the ion. A wide detector lines...
• The figure shows the essentials of a mass spectrometer, which can be used to measure the mass of an ion; an ion of mass m (to be measured) and charge q is produced in source S. The initially stationary ion is accelerated by the electric field due to a potential difference V. The ion leaves S and enters a separator chamber in which a uniform magnetic field is perpendicular to the path of the ion. A wide detector lines...
The atomic masses of three elements are given below, where 1 u = 1.6605 x 10-27...
The atomic masses of three elements are given below, where 1 u = 1.6605 x 10-27 kg. What are the frequencies of the circular motion (cyclotron frequencies) of the following three molecules in a 2.0000 T magnetic field, to 5 significant figures? Atomic mass of 12C: 12.000u, 14N: 14.003u, 16O: 19.995u a) O2+ b) N2+ c) CO+
The picture above shows part of a mass spectrometer that can be used to measure molecular...
The picture above shows part of a mass spectrometer that can be used to measure molecular charge-to-mass ratios. A charged molecule (orange circle) is ionized and accelerated through an electric potential difference into a region with a uniform magnetic field. Here the magnetic field points out of the screen. The field makes the positively charged molecules undergo circular motion as shown. By adjusting the voltage difference between the plates, one can change the radius of curvature of the charged particles...
+V 0V Detector The picture above shows part of a mass spectrometer that can be used...
 +V 0V Detector The picture above shows part of a mass spectrometer that can be used to measure molecular charge-to-mass ratios. A charged molecule (orange circle) is ionized and accelerated through an electric potential difference into a region with a uniform magnetic field. Here the magnetic field points out of the screen. The field makes the positively charged molecules undergo circular motion as shown. By adjusting the voltage difference between the plates, one can change the radius of curvature of...
+V 0V Detector The picture above shows part of a mass spectrometer that can be used to measure molecular charge-to-mass ratios. A charged molecule (orange circle) is ionized and accelerated through an electric potential difference into a region with a uniform magnetic field. Here the magnetic field points out of the screen. The field makes the positively charged molecules undergo circular motion as shown. By adjusting the voltage difference between the plates, one can change the radius of curvature of...
One type of mass spectrometer accelerates ions of charge q, mass m, and initial speed zero...
One type of mass spectrometer accelerates ions of charge q, mass m, and initial speed zero through a potential difference ΔV. The ions then enter a magnetic field where they move in a circular path of radius r. How is the mass of the ions related to these other quantities? Express your answer in terms of the variables q, r, B, and ΔV.
The ions entering the mass spectrometer have the same charges. After being accelerated through a potential...
 The ions entering the mass spectrometer have the same charges. After being accelerated through a potential difference of 2.30 KV. singly charged 12ction moves in a circle of radius 111 cm in the magnetic field of a mass spectrometer. What is the magnitude of the field? Use these atomic mass values: 12c, 12.0 u: 14C, 14.0 u: 160, 15.99 u. The conversion between atomic mass units and kilograms is 1 u = 1.66 x 10-27 kg T
The ions entering the mass spectrometer have the same charges. After being accelerated through a potential difference of 2.30 KV. singly charged 12ction moves in a circle of radius 111 cm in the magnetic field of a mass spectrometer. What is the magnitude of the field? Use these atomic mass values: 12c, 12.0 u: 14C, 14.0 u: 160, 15.99 u. The conversion between atomic mass units and kilograms is 1 u = 1.66 x 10-27 kg T
In a mass spectrometer chlorine ions of mass 35u and charge +5e are emitted from a source and accelerated thro...
In a mass spectrometer chlorine ions of mass 35u and charge +5e are emitted from a source and accelerated through a potential difference of 250 kV. They then enter a region with a magnetic field which is perpendicular to their original direction of motion. The chlorine ions exit the spectrometer after being bent along a path with radius of curvature 3.5 m. What is the value of the magnetic field? (u = 1.66 ´ 10–27 kg, e = 1.6 ´...
Constants Part A A mass spectrograph is used to measure the masses of ions, or to...
 Constants Part A A mass spectrograph is used to measure the masses of ions, or to separate ions of different masses. In one design for such an instrument, ions with mass m and charge q are accelerated through a potential difference V. They then enter a uniform magnetic field that is perpendicular to their velocity and are deflected in a semicircular path of radius R. A detector measures where the ions complete the semicircle and from this it is easy...
Constants Part A A mass spectrograph is used to measure the masses of ions, or to separate ions of different masses. In one design for such an instrument, ions with mass m and charge q are accelerated through a potential difference V. They then enter a uniform magnetic field that is perpendicular to their velocity and are deflected in a semicircular path of radius R. A detector measures where the ions complete the semicircle and from this it is easy...
Most questions answered within 3 hours.
-
What is meant by a “term premium”?
What can explain such a premium? Is it a...
asked 50 minutes ago -
23. Which molecule has only covalent bonds? A. CO2 B. Al2O3 C.
Mg3N2
24. The octet...
asked 1 hour ago -
the
total pressure for a mixture of N2O4 and NO2 is 2.20 atm. If Kp=
7.10...
asked 1 hour ago -
Delaware Corp. prepared a master budget that included $22,385
for direct materials, $28,600 for direct labor,...
asked 1 hour ago -
For pesticide HCB (hexachlorobenzene), its logarithmic partition
coefficient log Kow is 5.6. What would be the...
asked 1 hour ago -
A chemist requires 0.422 mil Na2CO3 for a reaction. How many
grams does this correspond to?
asked 1 hour ago -
If the vapor pressure of carvone is approximately 9.4 torr at 99
°C, approximately how much...
asked 1 hour ago -
A juice bottling company is carrying out a test at 10%
significance that the mean population...
asked 1 hour ago -
What is the reflectivity (in percent) needed to keep water at a
temperature near its freezing...
asked 1 hour ago -
Suppose that the average surface temperature of Earth is 300K.
Assume this is uniform over its...
asked 1 hour ago -
Draw the condensed structural formula for alkenes and alkynes or
the line-angle structural formula for cycloalkenes...
asked 1 hour ago -
M. Laing has suggested a new arrangement of the periodic table
(J.Chem.Ed.1989, 66,
746). Answer the following...
asked 2 hours ago
 To five significant figures, what accelerating potential difference AV is required to detect the ion 0 ? The masses of the atoms are shown in the table; the mass of the missing electron is less than 0.001 u and is not relevant at this level of precision. Use the following constants: 1 u = 1.6605 x 10-27 kg, e = 1.6022 x 10-19 C. (Figure 1) shows a mass spectrometer, an analytical instrument used to identify the various molecules in...
To five significant figures, what accelerating potential difference AV is required to detect the ion 0 ? The masses of the atoms are shown in the table; the mass of the missing electron is less than 0.001 u and is not relevant at this level of precision. Use the following constants: 1 u = 1.6605 x 10-27 kg, e = 1.6022 x 10-19 C. (Figure 1) shows a mass spectrometer, an analytical instrument used to identify the various molecules in...
 • The figure shows the essentials of a mass spectrometer, which can be used to measure the mass of an ion; an ion of mass m (to be measured) and charge q is produced in source S. The initially stationary ion is accelerated by the electric field due to a potential difference V. The ion leaves S and enters a separator chamber in which a uniform magnetic field is perpendicular to the path of the ion. A wide detector lines...
• The figure shows the essentials of a mass spectrometer, which can be used to measure the mass of an ion; an ion of mass m (to be measured) and charge q is produced in source S. The initially stationary ion is accelerated by the electric field due to a potential difference V. The ion leaves S and enters a separator chamber in which a uniform magnetic field is perpendicular to the path of the ion. A wide detector lines...
 +V 0V Detector The picture above shows part of a mass spectrometer that can be used to measure molecular charge-to-mass ratios. A charged molecule (orange circle) is ionized and accelerated through an electric potential difference into a region with a uniform magnetic field. Here the magnetic field points out of the screen. The field makes the positively charged molecules undergo circular motion as shown. By adjusting the voltage difference between the plates, one can change the radius of curvature of...
+V 0V Detector The picture above shows part of a mass spectrometer that can be used to measure molecular charge-to-mass ratios. A charged molecule (orange circle) is ionized and accelerated through an electric potential difference into a region with a uniform magnetic field. Here the magnetic field points out of the screen. The field makes the positively charged molecules undergo circular motion as shown. By adjusting the voltage difference between the plates, one can change the radius of curvature of...
 The ions entering the mass spectrometer have the same charges. After being accelerated through a potential difference of 2.30 KV. singly charged 12ction moves in a circle of radius 111 cm in the magnetic field of a mass spectrometer. What is the magnitude of the field? Use these atomic mass values: 12c, 12.0 u: 14C, 14.0 u: 160, 15.99 u. The conversion between atomic mass units and kilograms is 1 u = 1.66 x 10-27 kg T
The ions entering the mass spectrometer have the same charges. After being accelerated through a potential difference of 2.30 KV. singly charged 12ction moves in a circle of radius 111 cm in the magnetic field of a mass spectrometer. What is the magnitude of the field? Use these atomic mass values: 12c, 12.0 u: 14C, 14.0 u: 160, 15.99 u. The conversion between atomic mass units and kilograms is 1 u = 1.66 x 10-27 kg T
 Constants Part A A mass spectrograph is used to measure the masses of ions, or to separate ions of different masses. In one design for such an instrument, ions with mass m and charge q are accelerated through a potential difference V. They then enter a uniform magnetic field that is perpendicular to their velocity and are deflected in a semicircular path of radius R. A detector measures where the ions complete the semicircle and from this it is easy...
Constants Part A A mass spectrograph is used to measure the masses of ions, or to separate ions of different masses. In one design for such an instrument, ions with mass m and charge q are accelerated through a potential difference V. They then enter a uniform magnetic field that is perpendicular to their velocity and are deflected in a semicircular path of radius R. A detector measures where the ions complete the semicircle and from this it is easy...