Consider the following competing hypotheses and accompanying sample data drawn independently from normally distributed populations. (Note:...
|
Consider the following competing hypotheses and accompanying sample data drawn independently from normally distributed populations. (Note: the automated question following this one will ask you confidence interval questions for this same data, so jot down your work.) |
| H0: μ1 − μ2 = 0 |
| HA: μ1 − μ2 ≠ 0 |
| x−1x−1 = 60 | x−2x−2 = 56 |
| σ1 = 1.62 | σ2 = 10.20 |
| n1 = 25 | n2 = 25 |
|
Calculate the value of the test statistic. (Negative values should be indicated by a minus sign. Round intermediate calculations to 4 decimal places and final answer to 2 decimal places.) |
| Test statistic |
| a-2. | Calculate the p-value of the test statistic. Remember: because this is a two-tailed hypothesis test, you must double your p-value that will be compared with α in the hypothesis test criteria. (Round your answer to 4 decimal places.) |
| p-value |
| a-3. | Do you reject the null hypothesis at the 1% level? |
|
| b. | Using the critical value approach, can we reject the null hypothesis at the 1% level? |
|
Now provide confidence interval information from the previous question. Specifically:
a. What is the value of the point estimate of the difference between the two population means?
b. What is the margin of error at 90% confidence?
(± what value; please provide to 4 decimals; e.g. "3.1234")
c. With that margin of error, what is the low number in the confidence interval?
d. With that margin of error, what is the high number in the confidence interval?
Homework Answers
Add Answer to:
Consider the following competing hypotheses and accompanying
sample data drawn independently from normally distributed
populations. (Note:...
Consider the following competing hypotheses and accompanying sample data drawn independently from normally distributed populations. (You may find it useful to reference the appropriate table: z table or t table)
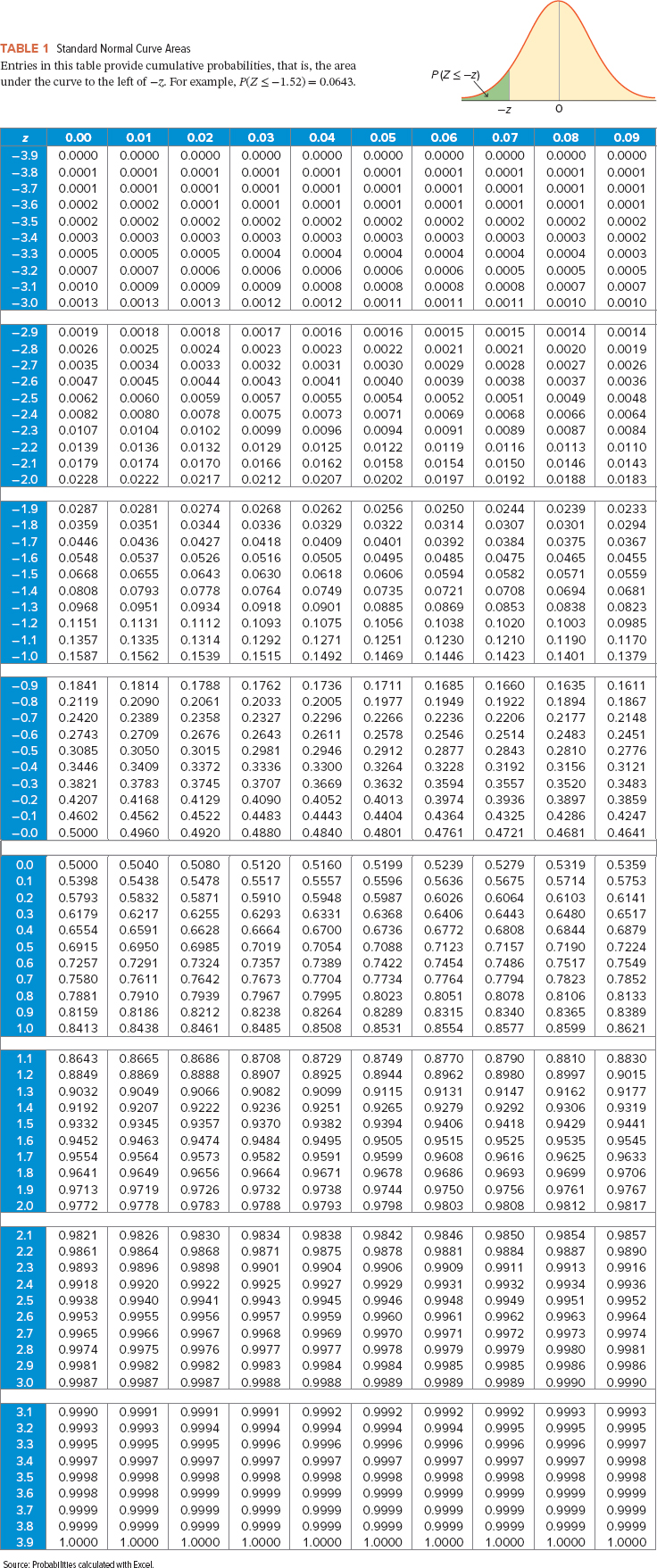 Consider the following competing hypotheses and accompanying sample data drawn independently from normally distributed populations. (You may find it useful to reference the appropriate table: z table or t table) H0: μ1 − μ2 ≥ 0HA: μ1 − μ2 < 0 x¯1x¯1= 249x−2x−2= 262s1 = 35s2 = 23n1 = 10n2 = 10a-1. Calculate the value of the test statistic under the assumption that the population variances are equal. (Negative values should be indicated by a minus sign. Round all intermediate calculations to at least 4 decimal places and final answer to 3 decimal places.) a-2. Find the p-value. multiple choice 1p-value < 0.010.01 ≤ p-value...
Consider the following competing hypotheses and accompanying sample data drawn independently from normally distributed populations. (You may find it useful to reference the appropriate table: z table or t table) H0: μ1 − μ2 ≥ 0HA: μ1 − μ2 < 0 x¯1x¯1= 249x−2x−2= 262s1 = 35s2 = 23n1 = 10n2 = 10a-1. Calculate the value of the test statistic under the assumption that the population variances are equal. (Negative values should be indicated by a minus sign. Round all intermediate calculations to at least 4 decimal places and final answer to 3 decimal places.) a-2. Find the p-value. multiple choice 1p-value < 0.010.01 ≤ p-value...
Consider the following competing hypotheses and accompanying sample data drawn independently from normally distributed populations. (You...
 Consider the following competing hypotheses and accompanying sample data drawn independently from normally distributed populations. (You may find it useful to reference the appropriate table: z table or t table) Ho: H1-Hu2 0 HA: H1 Hz< e 251 252 s1 39 s=19 n1=7 n 7 a-1. Calculate the value of the test statistic under the assumption that the population variances are equal. (Negative values should be indicated by a minus sign. Round all intermediate calculations to at least 4 decimal...
Consider the following competing hypotheses and accompanying sample data drawn independently from normally distributed populations. (You may find it useful to reference the appropriate table: z table or t table) Ho: H1-Hu2 0 HA: H1 Hz< e 251 252 s1 39 s=19 n1=7 n 7 a-1. Calculate the value of the test statistic under the assumption that the population variances are equal. (Negative values should be indicated by a minus sign. Round all intermediate calculations to at least 4 decimal...
Consider the following competing hypotheses and accompanying sample data drawn independently from normally distributed populations
 Consider the following competing hypotheses and accompanying sample data drawn independently from normally distributed populations. (You may find it useful to reference the appropriate table: ztable or ttable) a-1. Calculate the value of the test statistic. (Negative values should be indicated by a minus sign. Round all intermediate calculations to at least 4 decimal places and final answer to 2 decimal places.) Test statistic a-2. Find the p-value.a-3. Do you reject the null hypothesis at the 1% significance level? a-4. Interpret the results...
Consider the following competing hypotheses and accompanying sample data drawn independently from normally distributed populations. (You may find it useful to reference the appropriate table: ztable or ttable) a-1. Calculate the value of the test statistic. (Negative values should be indicated by a minus sign. Round all intermediate calculations to at least 4 decimal places and final answer to 2 decimal places.) Test statistic a-2. Find the p-value.a-3. Do you reject the null hypothesis at the 1% significance level? a-4. Interpret the results...
Consider the following sample data drawn independently from normally distributed populations with equal population variances. Use...
 Consider the following sample data drawn independently from normally distributed populations with equal population variances. Use Table 2. Sample 1 12.7 11.7 7.8 11.6 10.8 10.4 94 10.7 Sample 2 8.7 10.8 13.5 11.8 11.5 95 10.8 11.8 Click here for the Excel Data File a. Construct the relevant hypotheses to test if the mean of the second population is greater than the mean of the first population. O Ho: Ni - M2 = 0; HAV1 -20 O Ho: Mi...
Consider the following sample data drawn independently from normally distributed populations with equal population variances. Use Table 2. Sample 1 12.7 11.7 7.8 11.6 10.8 10.4 94 10.7 Sample 2 8.7 10.8 13.5 11.8 11.5 95 10.8 11.8 Click here for the Excel Data File a. Construct the relevant hypotheses to test if the mean of the second population is greater than the mean of the first population. O Ho: Ni - M2 = 0; HAV1 -20 O Ho: Mi...
Consider the following data drawn independently from normally distributed populations: (You may find it useful to...
Consider the following data drawn independently from normally distributed populations: (You may find it useful to reference the appropriate table: z table or t table) x−1x−1 = 27.7 x−2x−2 = 30.1 σ12 = 92.8 σ22 = 87.5 n1 = 24 n2 = 33 a. Construct the 99% confidence interval for the difference between the population means. (Negative values should be indicated by a minus sign. Round all intermediate calculations to at least 4 decimal places and final answers to 2...
Consider the following competing hypotheses and accompanying sample data drawn independently from normally distributed populations
 Consider the following competing hypotheses and accompanying sample data drawn independently from normally distributed populations. (You may find it useful to reference the appropriate table: z table or t table) a-1. Calculate the value of the test statistic.a-2. Find the p-value.a-3. Do you reject the null hypothesis at the 5% significance level? a-4. Interpret the results at α = 0.05.
Consider the following competing hypotheses and accompanying sample data drawn independently from normally distributed populations. (You may find it useful to reference the appropriate table: z table or t table) a-1. Calculate the value of the test statistic.a-2. Find the p-value.a-3. Do you reject the null hypothesis at the 5% significance level? a-4. Interpret the results at α = 0.05.
Consider the following competing hypotheses and accompanying sample data drawn independently from normally distributed populations. (You...
Consider the following competing hypotheses and accompanying sample data drawn independently from normally distributed populations. (You may find it useful to reference the appropriate table: z table or t table) H0: μ1 − μ2 ≥ 0 HA: μ1 − μ2 < 0 x−1 x − 1 = 222 x−2 x − 2 = 253 s1 = 32 s2 = 26 n1 = 12 n2 = 12 a-1. Calculate the value of the test statistic under the assumption that the population...
Assume that both populations are normally distributed
 Assume that both populations are normally distributed(a) Test whether μ1 ≠ μ2 at the α=0.05 level of significance for the given sample data(b) Construct a 95 % confidence interval about μ1-μ2.(a) Test whether μ1 ≠ P2 at the α=0.05 level of significance for the given sample data. Determine the null and alternative hypothesis for this test.Determine the P-value for this hypothesis test.P=_______ (Round to threes decimal places as needed.)Should the null hypothesis be rejected?A. Reject H0, there is not sufficient...
Assume that both populations are normally distributed(a) Test whether μ1 ≠ μ2 at the α=0.05 level of significance for the given sample data(b) Construct a 95 % confidence interval about μ1-μ2.(a) Test whether μ1 ≠ P2 at the α=0.05 level of significance for the given sample data. Determine the null and alternative hypothesis for this test.Determine the P-value for this hypothesis test.P=_______ (Round to threes decimal places as needed.)Should the null hypothesis be rejected?A. Reject H0, there is not sufficient...
1.3.3 Question Help * Sample 1 Sample 2 Assume that both populations are normally distributed. a)...
 1.3.3 Question Help * Sample 1 Sample 2 Assume that both populations are normally distributed. a) Test whether μ? μ2 at the α 0.05 level of significance for the given sample data. b) Construct a 95% confidence interval about μ1-2. 16 44.1 12.4 52.5 9.7 EB Click the icon to view the Student t-distribution table a) Perform a hypothesis test. Determine the null and alternative hypotheses Determine the critical value(s). Select the correct choice bElow and fill in the answer...
1.3.3 Question Help * Sample 1 Sample 2 Assume that both populations are normally distributed. a) Test whether μ? μ2 at the α 0.05 level of significance for the given sample data. b) Construct a 95% confidence interval about μ1-2. 16 44.1 12.4 52.5 9.7 EB Click the icon to view the Student t-distribution table a) Perform a hypothesis test. Determine the null and alternative hypotheses Determine the critical value(s). Select the correct choice bElow and fill in the answer...
Use the given statistics to complete parts (a) and (b). Assume that the populations are normally...
Use the given statistics to complete parts (a) and (b). Assume that the populations are normally distributed. Population 1 Population 2 n 26 16 x 49.8 40.1 s 6.8 13.2 (a) Test whether μ1 > μ2 at the α = 0.01 level of significance for the given sample data. (b) Construct a 90% confidence interval about μ1 − μ2 . (a) Identify the null and alternative hypotheses for this test. A. H0 : μ1 ≠...
Most questions answered within 3 hours.
-
Compare and contrast the linear motion and angular motion
equations F ma and . That is,...
asked 2 minutes ago -
Now that this course has taken you on a journey of introduction
to the world of...
asked 43 minutes ago -
Given a regression sum of squares equal to 2373.59 and a total
sum of squares equal...
asked 56 minutes ago -
The sandwich maker of the EE-Cole-Eye Sandwich Truck was just
fired (for a reason described below)...
asked 3 hours ago -
Name the following coordination compounds using systematic
nomenclature.
1. [Co(H2O)6]Cl2:
2. [Cr(NH3)6](NO3)3:
3. K4[Fe(CN)6]:
4. Na[Au(CN)4]:...
asked 2 hours ago -
Propose an efficient synthesis of 2-Bromo-5-nitrotoluene from
benzene. Hint: 3 steps. Consider directing effects of substituents....
asked 4 hours ago -
This assignment will explore the impact of corporate decisions
on a local versus a global perspective....
asked 3 hours ago -
Given the function below, F(w,x,y,z)= x’z+w’z’+w’y
a) draw a logic diagram for an implementation which uses...
asked 3 hours ago -
Most political philosophers believe we have a duty to obey laws,
even if the laws in...
asked 4 hours ago -
Which of the following are common negotiation outcome
mistakes?
a. Leave money on the table b....
asked 4 hours ago -
Convert the following quantities:
a) 0.819 atm to torr b) 512 mmHg to bar c) 11.2...
asked 5 hours ago -
C ++ Implement cat command
The purpose of this assignment is to provide practice using the...
asked 5 hours ago

 Consider the following competing hypotheses and accompanying sample data drawn independently from normally distributed populations. (You may find it useful to reference the appropriate table: z table or t table) Ho: H1-Hu2 0 HA: H1 Hz< e 251 252 s1 39 s=19 n1=7 n 7 a-1. Calculate the value of the test statistic under the assumption that the population variances are equal. (Negative values should be indicated by a minus sign. Round all intermediate calculations to at least 4 decimal...
Consider the following competing hypotheses and accompanying sample data drawn independently from normally distributed populations. (You may find it useful to reference the appropriate table: z table or t table) Ho: H1-Hu2 0 HA: H1 Hz< e 251 252 s1 39 s=19 n1=7 n 7 a-1. Calculate the value of the test statistic under the assumption that the population variances are equal. (Negative values should be indicated by a minus sign. Round all intermediate calculations to at least 4 decimal...
 Consider the following sample data drawn independently from normally distributed populations with equal population variances. Use Table 2. Sample 1 12.7 11.7 7.8 11.6 10.8 10.4 94 10.7 Sample 2 8.7 10.8 13.5 11.8 11.5 95 10.8 11.8 Click here for the Excel Data File a. Construct the relevant hypotheses to test if the mean of the second population is greater than the mean of the first population. O Ho: Ni - M2 = 0; HAV1 -20 O Ho: Mi...
Consider the following sample data drawn independently from normally distributed populations with equal population variances. Use Table 2. Sample 1 12.7 11.7 7.8 11.6 10.8 10.4 94 10.7 Sample 2 8.7 10.8 13.5 11.8 11.5 95 10.8 11.8 Click here for the Excel Data File a. Construct the relevant hypotheses to test if the mean of the second population is greater than the mean of the first population. O Ho: Ni - M2 = 0; HAV1 -20 O Ho: Mi...
 Assume that both populations are normally distributed(a) Test whether μ1 ≠ μ2 at the α=0.05 level of significance for the given sample data(b) Construct a 95 % confidence interval about μ1-μ2.(a) Test whether μ1 ≠ P2 at the α=0.05 level of significance for the given sample data. Determine the null and alternative hypothesis for this test.Determine the P-value for this hypothesis test.P=_______ (Round to threes decimal places as needed.)Should the null hypothesis be rejected?A. Reject H0, there is not sufficient...
Assume that both populations are normally distributed(a) Test whether μ1 ≠ μ2 at the α=0.05 level of significance for the given sample data(b) Construct a 95 % confidence interval about μ1-μ2.(a) Test whether μ1 ≠ P2 at the α=0.05 level of significance for the given sample data. Determine the null and alternative hypothesis for this test.Determine the P-value for this hypothesis test.P=_______ (Round to threes decimal places as needed.)Should the null hypothesis be rejected?A. Reject H0, there is not sufficient...
 1.3.3 Question Help * Sample 1 Sample 2 Assume that both populations are normally distributed. a) Test whether μ? μ2 at the α 0.05 level of significance for the given sample data. b) Construct a 95% confidence interval about μ1-2. 16 44.1 12.4 52.5 9.7 EB Click the icon to view the Student t-distribution table a) Perform a hypothesis test. Determine the null and alternative hypotheses Determine the critical value(s). Select the correct choice bElow and fill in the answer...
1.3.3 Question Help * Sample 1 Sample 2 Assume that both populations are normally distributed. a) Test whether μ? μ2 at the α 0.05 level of significance for the given sample data. b) Construct a 95% confidence interval about μ1-2. 16 44.1 12.4 52.5 9.7 EB Click the icon to view the Student t-distribution table a) Perform a hypothesis test. Determine the null and alternative hypotheses Determine the critical value(s). Select the correct choice bElow and fill in the answer...