Consider the following competing hypotheses and accompanying sample data. (You may find it useful to reference...
Consider the following competing hypotheses and accompanying sample data. (You may find it useful to reference the appropriate table: z table or t table) H0: p1 − p2 ≥ 0 HA: p1 − p2 < 0 x1 = 250 x2 = 275 n1 = 400 n2 = 400 a. Calculate the value of the test statistic. (Negative value should be indicated by a minus sign. Round intermediate calculations to at least 4 decimal places and final answer to 2 decimal places.) b. Find the p-value. p-value < 0.01 0.01 ≤ p-value < 0.025 0.025 ≤ p-value < 0.05 0.05 ≤ p-value < 0.10 p-value ≥ 0.10 c. At the 5% significance level, what is the conclusion to the test? Reject H0 since the p-value is less than significance level. Reject H0 since the p-value is greater than significance level. Do not reject H0 since the p-value is less than significance level. Do not reject H0 since the p-value is greater than significance level. d. Interpret the results at α = 0.05. We conclude that the population proportions differ. We cannot conclude that the population proportions differ. We conclude that population proportion 2 is greater than population proportion 1. We cannot conclude that population proportion 2 is greater than population proportion 1.
Homework Answers
Given that,
sample one, x1 =250, n1 =400, p1= x1/n1=0.625
sample two, x2 =275, n2 =400, p2= x2/n2=0.688
null, Ho: p1 >= p2
alternate, H1: p1 < p2
level of significance, α = 0.05
from standard normal table,left tailed z α/2 =1.64
since our test is left-tailed
reject Ho, if zo < -1.64
we use test statistic (z) = (p1-p2)/√(p^q^(1/n1+1/n2))
zo =(0.625-0.688)/sqrt((0.656*0.344(1/400+1/400))
zo =-1.861
| zo | =1.861
critical value
the value of |z α| at los 0.05% is 1.64
we got |zo| =1.861 & | z α | =1.64
make decision
hence value of | zo | > | z α| and here we reject Ho
p-value: left tail - Ha : ( p < -1.861 ) = 0.03137
hence value of p0.05 > 0.03137,here we reject Ho
ANSWERS
---------------
null, Ho: p1 >= p2
alternate, H1: p1 < p2
test statistic: -1.861
critical value: -1.64
decision: reject Ho
p-value: 0.03137
Reject H0 since the p-value is less than significance level
we have enough evidence to support the claim that population
proportion 2 is greater than population proportion 1
Add Answer to:
Consider the following competing hypotheses and accompanying
sample data. (You may find it useful to reference...
Consider the following competing hypotheses and accompanying sample data (You may find it useful to reference...
 Consider the following competing hypotheses and accompanying sample data (You may find it useful to reference the appropriate table: z table or t table) Ho: Pi - P22 MA: P1 - P2 @ X1 - 238 nu - 425 X2 - 263 n2 - 425 a. Calculate the value of the test statistic (Negative value should be indicated by a minus sign. Round intermediate calculations to at least 4 decimal places and final answer to 2 decimal places.) Test statistic...
Consider the following competing hypotheses and accompanying sample data (You may find it useful to reference the appropriate table: z table or t table) Ho: Pi - P22 MA: P1 - P2 @ X1 - 238 nu - 425 X2 - 263 n2 - 425 a. Calculate the value of the test statistic (Negative value should be indicated by a minus sign. Round intermediate calculations to at least 4 decimal places and final answer to 2 decimal places.) Test statistic...
Consider the following competing hypotheses and accompanying sample data drawn independently from normally distributed populations. (You may find it useful to reference the appropriate table: z table or t table)
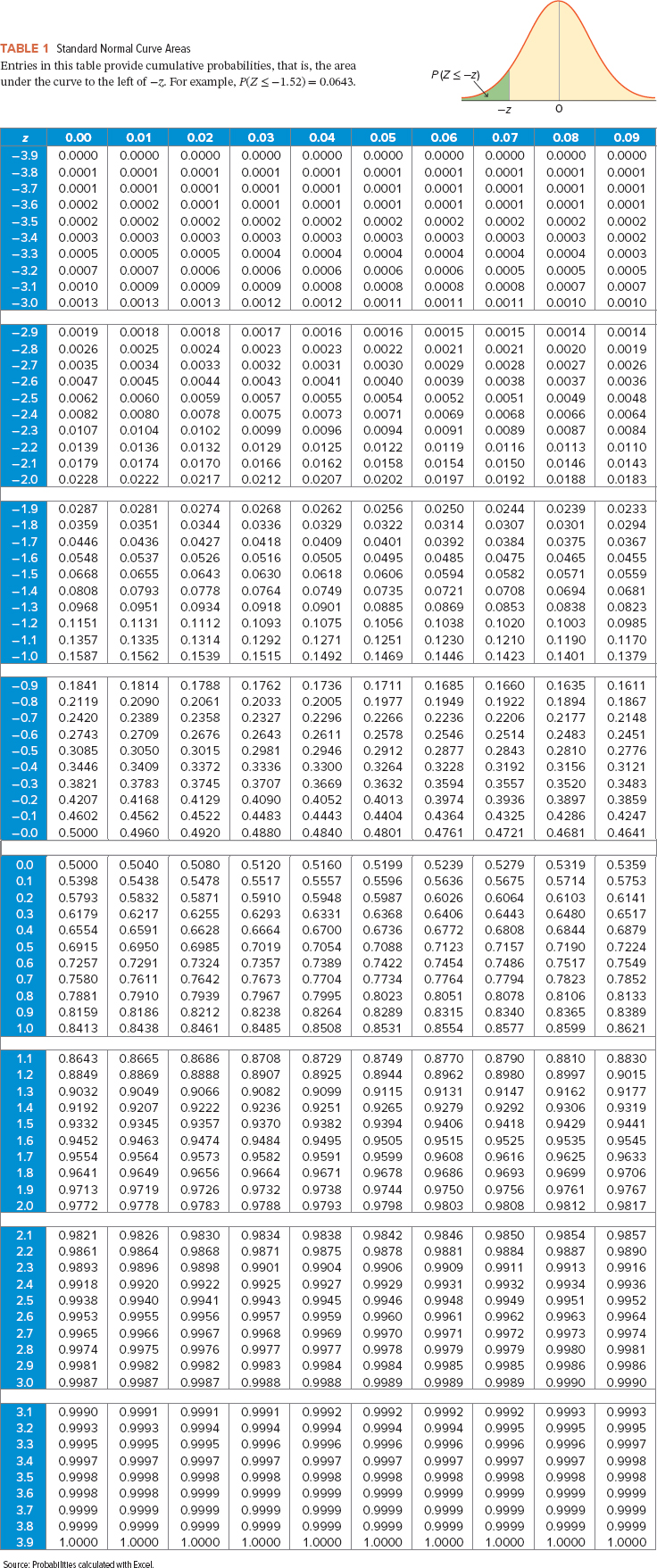 Consider the following competing hypotheses and accompanying sample data drawn independently from normally distributed populations. (You may find it useful to reference the appropriate table: z table or t table) H0: μ1 − μ2 ≥ 0HA: μ1 − μ2 < 0 x¯1x¯1= 249x−2x−2= 262s1 = 35s2 = 23n1 = 10n2 = 10a-1. Calculate the value of the test statistic under the assumption that the population variances are equal. (Negative values should be indicated by a minus sign. Round all intermediate calculations to at least 4 decimal places and final answer to 3 decimal places.) a-2. Find the p-value. multiple choice 1p-value < 0.010.01 ≤ p-value...
Consider the following competing hypotheses and accompanying sample data drawn independently from normally distributed populations. (You may find it useful to reference the appropriate table: z table or t table) H0: μ1 − μ2 ≥ 0HA: μ1 − μ2 < 0 x¯1x¯1= 249x−2x−2= 262s1 = 35s2 = 23n1 = 10n2 = 10a-1. Calculate the value of the test statistic under the assumption that the population variances are equal. (Negative values should be indicated by a minus sign. Round all intermediate calculations to at least 4 decimal places and final answer to 3 decimal places.) a-2. Find the p-value. multiple choice 1p-value < 0.010.01 ≤ p-value...
Consider the following competing hypotheses: (You may find it useful to reference the appropriate table: z...
Consider the following competing hypotheses: (You may find it useful to reference the appropriate table: z table or t table) H0: μD ≥ 0; HA: μD < 0 d¯d¯ = −3.2, sD = 6.0, n = 23 The following results are obtained using matched samples from two normally distributed populations: a-1. Calculate the value of the test statistic, assuming that the sample difference is normally distributed. (Negative value should be indicated by a minus sign. Round intermediate calculations to at least...
Consider the following competing hypotheses and accompanying sample data. (You may find it useful to reference...
 Consider the following competing hypotheses and accompanying sample data. (You may find it useful to reference the a table: z table or ttable) He: P1 - P2 = 0.20 HA: P1 - P20.20 25 points *1 = 126 y = 243 X2 = 125 = 480 8 03.06.08 a. Calculate the value of the test statistic. (Round Intermediate calculations to at least 4 decimal places and final answer decimal places.) eBook Test statistic References b. Find the p-value. 0.01 s...
Consider the following competing hypotheses and accompanying sample data. (You may find it useful to reference the a table: z table or ttable) He: P1 - P2 = 0.20 HA: P1 - P20.20 25 points *1 = 126 y = 243 X2 = 125 = 480 8 03.06.08 a. Calculate the value of the test statistic. (Round Intermediate calculations to at least 4 decimal places and final answer decimal places.) eBook Test statistic References b. Find the p-value. 0.01 s...
Consider the following competing hypotheses and accompanying sample data drawn independently from normally distributed populations. (You...
 Consider the following competing hypotheses and accompanying sample data drawn independently from normally distributed populations. (You may find it useful to reference the appropriate table: z table or t table) Ho: H1-Hu2 0 HA: H1 Hz< e 251 252 s1 39 s=19 n1=7 n 7 a-1. Calculate the value of the test statistic under the assumption that the population variances are equal. (Negative values should be indicated by a minus sign. Round all intermediate calculations to at least 4 decimal...
Consider the following competing hypotheses and accompanying sample data drawn independently from normally distributed populations. (You may find it useful to reference the appropriate table: z table or t table) Ho: H1-Hu2 0 HA: H1 Hz< e 251 252 s1 39 s=19 n1=7 n 7 a-1. Calculate the value of the test statistic under the assumption that the population variances are equal. (Negative values should be indicated by a minus sign. Round all intermediate calculations to at least 4 decimal...
A multinomial experiment produced the following results: (You may find it useful to reference the appropriate...
 A multinomial experiment produced the following results:
(You may find it useful to reference the appropriate table:
chi-square table or F table)
Category
1
2
3
Frequency
117
100
83
a. Choose the appropriate alternative
hypothesis at H0: p1 =
0.50, p2 = 0.30, and p3 =
0.20.
All population proportions differ from their hypothesized
values.
At least one of the population proportions differs from its
hypothesized value.
b. Calculate the value of the test statistic.
(Round intermediate calculations to...
A multinomial experiment produced the following results:
(You may find it useful to reference the appropriate table:
chi-square table or F table)
Category
1
2
3
Frequency
117
100
83
a. Choose the appropriate alternative
hypothesis at H0: p1 =
0.50, p2 = 0.30, and p3 =
0.20.
All population proportions differ from their hypothesized
values.
At least one of the population proportions differs from its
hypothesized value.
b. Calculate the value of the test statistic.
(Round intermediate calculations to...
In order to conduct a hypothesis test for the population proportion, you sample 290 observations that...
In order to conduct a hypothesis test for the population proportion, you sample 290 observations that result in 87 successes. (You may find it useful to reference the appropriate table: z table or t table) H0: p ≥ 0.36; HA: p < 0.36. a-1. Calculate the value of the test statistic. (Negative value should be indicated by a minus sign. Round intermediate calculations to at least 4 decimal places and final answer to 2 decimal places.) a-2. Find the p-value....
Consider the following hypotheses: H0: μ ≥ 160 HA: μ < 160 The population is normally...
Consider the following hypotheses: H0: μ ≥ 160 HA: μ < 160 The population is normally distributed. A sample produces the following observations: 152 138 151 144 151 142 Conduct the test at the 1% level of significance. (You may find it useful to reference the appropriate table: z table or t table) a. Calculate the value of the test statistic. (Negative value should be indicated by a minus sign. Round intermediate calculations to at least 4 decimal places and...
In order to conduct a hypothesis test for the population proportion, you sample 450 observations that...
 In order to conduct a hypothesis test for the population
proportion, you sample 450 observations that result in 189
successes. (You may find it useful to reference the
appropriate table: z table or t
table)
H0: p ≥ 0.45;
HA: p < 0.45.
a-1. Calculate the value of the test statistic.
(Negative value should be indicated by a minus sign. Round
intermediate calculations to at least 4 decimal places and final
answer to 2 decimal places.)
TEST STATISTIC =
a-2....
In order to conduct a hypothesis test for the population
proportion, you sample 450 observations that result in 189
successes. (You may find it useful to reference the
appropriate table: z table or t
table)
H0: p ≥ 0.45;
HA: p < 0.45.
a-1. Calculate the value of the test statistic.
(Negative value should be indicated by a minus sign. Round
intermediate calculations to at least 4 decimal places and final
answer to 2 decimal places.)
TEST STATISTIC =
a-2....
Exercise 9-15 Algo Consider the following hypotheses: H0: μ ≥ 130 HA: μ < 130 A...
Exercise 9-15 Algo Consider the following hypotheses: H0: μ ≥ 130 HA: μ < 130 A sample of 74 observations results in a sample mean of 125. The population standard deviation is known to be 31. (You may find it useful to reference the appropriate table: z table or t table) a-1. Calculate the value of the test statistic. (Negative value should be indicated by a minus sign. Round intermediate calculations to at least 4 decimal places and final answer...
Most questions answered within 3 hours.
-
In the Metric System, the basic unit of measurement for length
is ___
In the Metric...
asked 1 minute ago -
A spatially uniform electric field varies in time according
to E = Eo + 3000 t,...
asked 1 minute ago -
A sample of C3H8 has 1.60×1024 H atoms.
How many carbon atoms does the sample contain?...
asked 8 minutes ago -
Discuss the sales orders process module(s) in the Enterprise
Resource Planning system. How does it contribute...
asked 10 minutes ago -
The position in an object as a function of time is given as ?
(?) =...
asked 11 minutes ago -
Design a class for python named PersonData with the following
member variables:
lastName
firstName
address
city...
asked 24 minutes ago -
How does use of the risk/need/responsivity model impact
effective rehabilitation services?
asked 28 minutes ago -
Your rich uncle has just given you a high school graduation
present of $900,000. The present,...
asked 31 minutes ago -
1=Write a program in C to get 16-bit data from Port-D and send
it to ports...
asked 29 minutes ago -
Calculate Ecell for the following reaction and conditions: 0.50
M Br2 (aq), 0.10 M Pb+2 (aq),...
asked 50 minutes ago -
There can be more than one correct answer.
Hypophysiotropic hormones:
A. released by the hypothalamus
B....
asked 55 minutes ago -
Scott Ruskin is the CEO of Decatur Materials. The company has
been struggling for the last...
asked 53 minutes ago
 Consider the following competing hypotheses and accompanying sample data (You may find it useful to reference the appropriate table: z table or t table) Ho: Pi - P22 MA: P1 - P2 @ X1 - 238 nu - 425 X2 - 263 n2 - 425 a. Calculate the value of the test statistic (Negative value should be indicated by a minus sign. Round intermediate calculations to at least 4 decimal places and final answer to 2 decimal places.) Test statistic...
Consider the following competing hypotheses and accompanying sample data (You may find it useful to reference the appropriate table: z table or t table) Ho: Pi - P22 MA: P1 - P2 @ X1 - 238 nu - 425 X2 - 263 n2 - 425 a. Calculate the value of the test statistic (Negative value should be indicated by a minus sign. Round intermediate calculations to at least 4 decimal places and final answer to 2 decimal places.) Test statistic...
 Consider the following competing hypotheses and accompanying sample data. (You may find it useful to reference the a table: z table or ttable) He: P1 - P2 = 0.20 HA: P1 - P20.20 25 points *1 = 126 y = 243 X2 = 125 = 480 8 03.06.08 a. Calculate the value of the test statistic. (Round Intermediate calculations to at least 4 decimal places and final answer decimal places.) eBook Test statistic References b. Find the p-value. 0.01 s...
Consider the following competing hypotheses and accompanying sample data. (You may find it useful to reference the a table: z table or ttable) He: P1 - P2 = 0.20 HA: P1 - P20.20 25 points *1 = 126 y = 243 X2 = 125 = 480 8 03.06.08 a. Calculate the value of the test statistic. (Round Intermediate calculations to at least 4 decimal places and final answer decimal places.) eBook Test statistic References b. Find the p-value. 0.01 s...
 Consider the following competing hypotheses and accompanying sample data drawn independently from normally distributed populations. (You may find it useful to reference the appropriate table: z table or t table) Ho: H1-Hu2 0 HA: H1 Hz< e 251 252 s1 39 s=19 n1=7 n 7 a-1. Calculate the value of the test statistic under the assumption that the population variances are equal. (Negative values should be indicated by a minus sign. Round all intermediate calculations to at least 4 decimal...
Consider the following competing hypotheses and accompanying sample data drawn independently from normally distributed populations. (You may find it useful to reference the appropriate table: z table or t table) Ho: H1-Hu2 0 HA: H1 Hz< e 251 252 s1 39 s=19 n1=7 n 7 a-1. Calculate the value of the test statistic under the assumption that the population variances are equal. (Negative values should be indicated by a minus sign. Round all intermediate calculations to at least 4 decimal...
 A multinomial experiment produced the following results:
(You may find it useful to reference the appropriate table:
chi-square table or F table)
Category
1
2
3
Frequency
117
100
83
a. Choose the appropriate alternative
hypothesis at H0: p1 =
0.50, p2 = 0.30, and p3 =
0.20.
All population proportions differ from their hypothesized
values.
At least one of the population proportions differs from its
hypothesized value.
b. Calculate the value of the test statistic.
(Round intermediate calculations to...
A multinomial experiment produced the following results:
(You may find it useful to reference the appropriate table:
chi-square table or F table)
Category
1
2
3
Frequency
117
100
83
a. Choose the appropriate alternative
hypothesis at H0: p1 =
0.50, p2 = 0.30, and p3 =
0.20.
All population proportions differ from their hypothesized
values.
At least one of the population proportions differs from its
hypothesized value.
b. Calculate the value of the test statistic.
(Round intermediate calculations to...
 In order to conduct a hypothesis test for the population
proportion, you sample 450 observations that result in 189
successes. (You may find it useful to reference the
appropriate table: z table or t
table)
H0: p ≥ 0.45;
HA: p < 0.45.
a-1. Calculate the value of the test statistic.
(Negative value should be indicated by a minus sign. Round
intermediate calculations to at least 4 decimal places and final
answer to 2 decimal places.)
TEST STATISTIC =
a-2....
In order to conduct a hypothesis test for the population
proportion, you sample 450 observations that result in 189
successes. (You may find it useful to reference the
appropriate table: z table or t
table)
H0: p ≥ 0.45;
HA: p < 0.45.
a-1. Calculate the value of the test statistic.
(Negative value should be indicated by a minus sign. Round
intermediate calculations to at least 4 decimal places and final
answer to 2 decimal places.)
TEST STATISTIC =
a-2....